In an era where health data is a cornerstone of medical advancement, the question of ownership—who controls, accesses, and benefits from your health information—has become a pivotal issue. This global debate intertwines patient rights, technological innovation, and regulatory frameworks, each vying to shape the future of healthcare.
The Patient’s Right: Ownership and Control
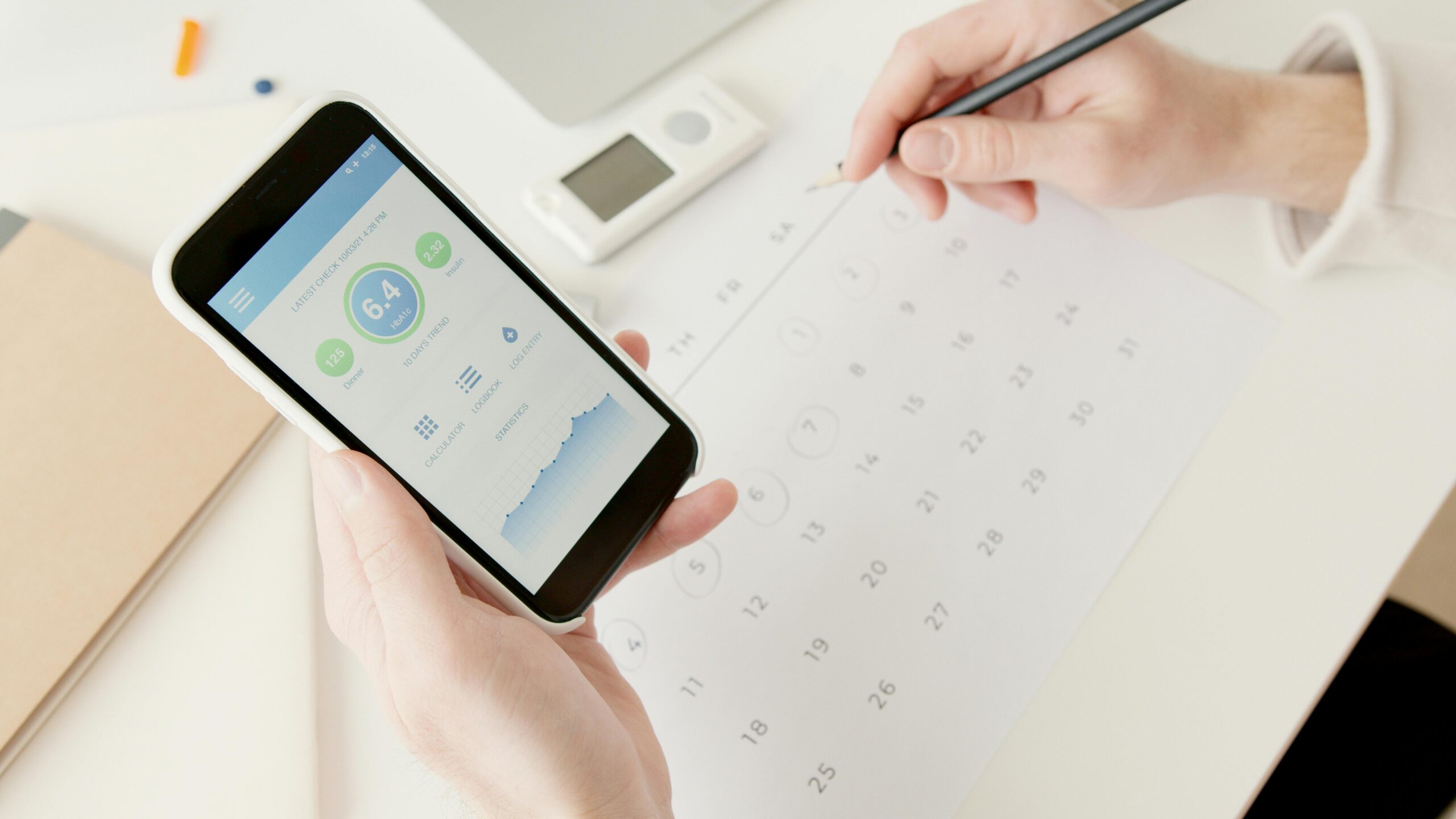
At the heart of this debate is the individual’s right to their health data. The European Union’s European Health Data Space (EHDS), effective since March 2025, grants EU citizens immediate access to their electronic health records, the ability to download them free of charge, and the option to delegate access to trusted parties. This regulation emphasizes patient autonomy, allowing individuals to restrict access, request corrections, and track who views their data .
Similarly, health record trusts are emerging as models where patients own and control their health data. These trusts enable individuals to maintain a lifetime electronic health record, adding personal notes, requesting corrections, and monitoring who accesses their information .
The Innovator’s Dilemma: Balancing Progress with Privacy
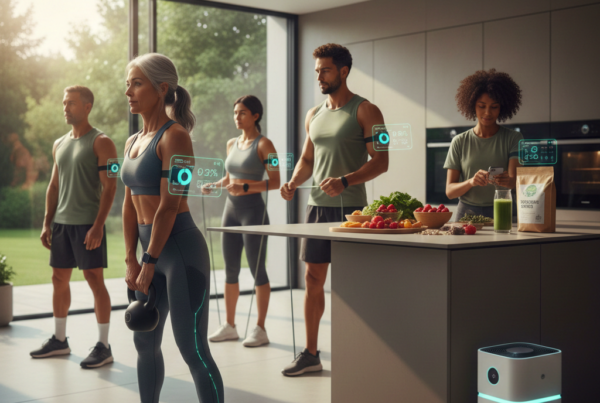
Technological advancements in digital therapeutics, AI-driven diagnostics, and personalized medicine rely heavily on access to vast amounts of health data. However, this necessity often clashes with privacy concerns. For instance, the UK’s proposal to establish a National Data Library to facilitate AI research using NHS data has raised alarms about potential breaches, re-identification risks, and the ethical use of anonymized data .
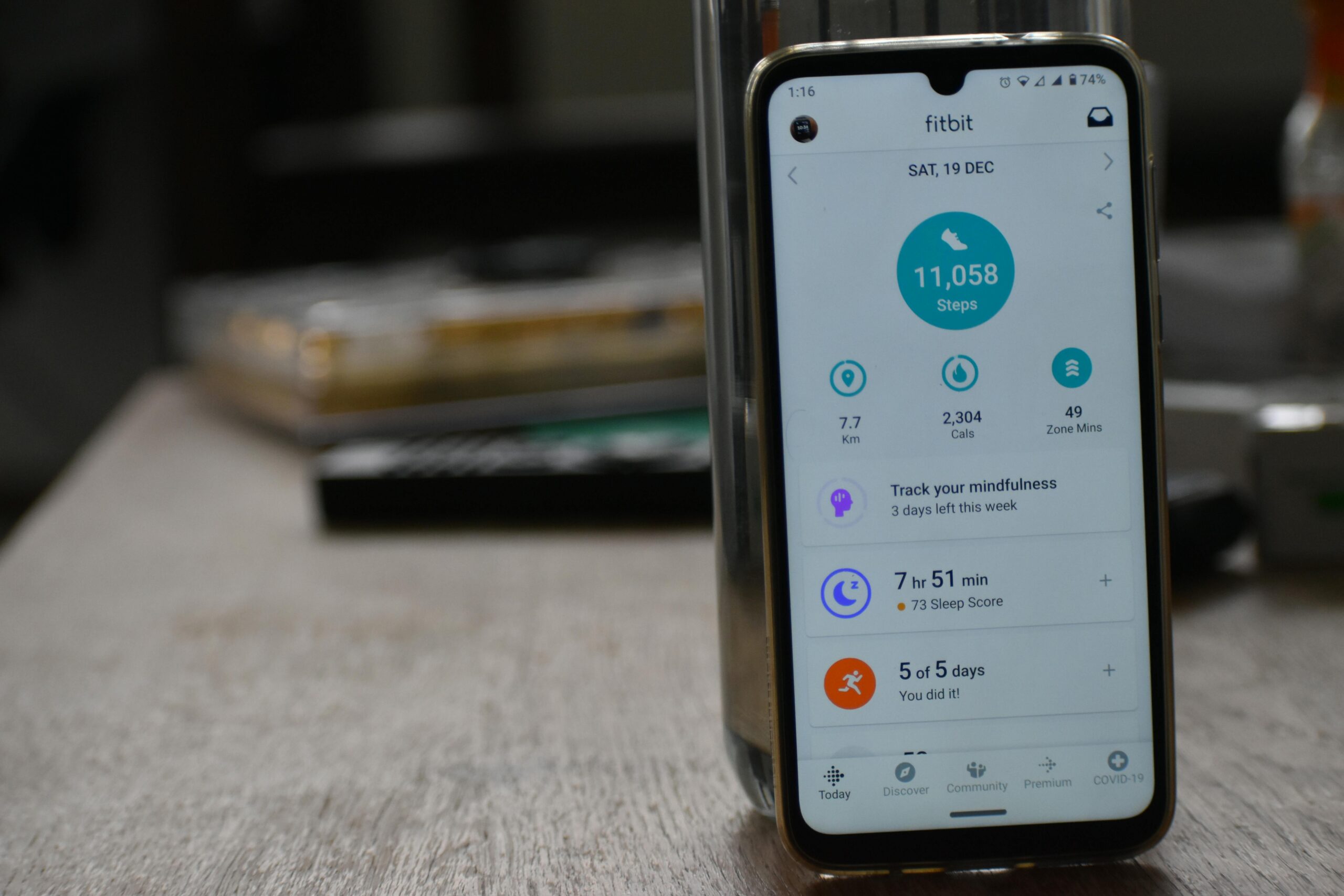
In the United States, the proliferation of health apps and fitness trackers has highlighted gaps in data protection. Many consumers mistakenly believe their data is protected under HIPAA, but most health apps fall outside its jurisdiction, leading to varied state-specific regulations governing health data privacy.
Regulatory Responses: Striving for a Global Consensus
Regulatory bodies worldwide are striving to balance innovation with privacy. The EU’s Data Governance Act and the EHDS aim to create a secure framework for data sharing, promoting interoperability while safeguarding individual rights .
In the UK, discussions around monetizing NHS data for research and AI development have sparked debates about the ethical implications and the need for stringent safeguards to protect patient privacy .
Technological Solutions: Empowering Patients
Innovative technologies are emerging to address the ownership dilemma. Blockchain, with its immutable ledger, offers a means for patients to control access to their health data securely. By tokenizing health records, individuals can grant or revoke access, ensuring transparency and accountability in data sharing .
Federated learning, a machine learning approach that allows models to be trained across decentralized devices without sharing raw data, is another promising solution. It enables the development of AI models while preserving data privacy, fostering an environment where innovation can thrive without compromising individual rights .
The future of health data ownership lies in collaborative governance models that involve patients, healthcare providers, technologists, and regulators. Health data trusts and cooperatives are emerging as institutions that define rules for data collection, processing, and sharing, ensuring that individuals retain control over their data while enabling its use for research and innovation .
As the global landscape evolves, the challenge will be to harmonize regulations, respect patient autonomy, and foster innovation. Only through inclusive dialogue and thoughtful policy-making can we navigate the complexities of health data ownership and unlock its full potential for societal benefit.