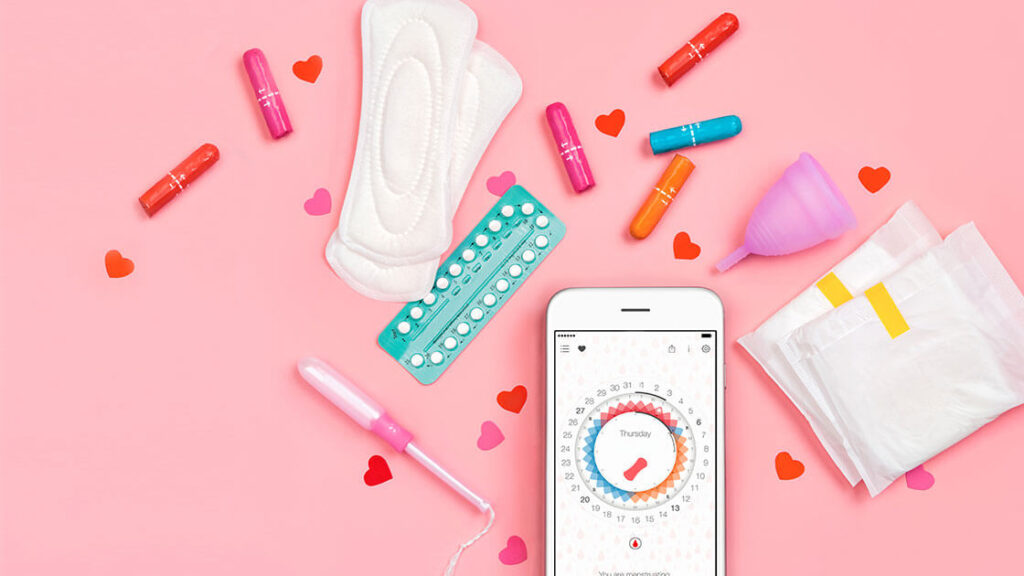
Maintaining proper menstrual hygiene is essential for both physical health and emotional well-being. Here are key practices related to menstrual hygiene that you should never ignore:
1. Change Sanitary Products Regularly
- Pads, tampons, or menstrual cups: Regardless of the menstrual product you use, it is important to change them regularly—usually every 4 to 6 hours for pads and tampons. Leaving products in for too long increases the risk of infections such as Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) or vaginal irritations.
- Overnight protection: If using pads overnight, ensure they are designed for overnight use to prevent leaks. Even overnight, try to change the pad as soon as you wake up.
2. Use the Right Sanitary Products
- Avoid highly scented products: Some scented pads or tampons may cause irritation or allergic reactions. Opt for unscented, breathable products that are free from chemicals.
- Choose the right absorbency: Ensure that you are using the right absorbency level for your flow. Too high absorbency can cause dryness and irritation, while too low absorbency can lead to leakage.
3. Maintain Proper Washing Habits
- Clean the genital area regularly: Wash the genital area (vulva) with lukewarm water at least twice a day during menstruation to keep it clean and fresh.
- Mild, unscented soap: If you use soap, choose one that is mild and free of fragrances or strong chemicals to prevent irritation.
- Avoid douching: Douching disrupts the natural balance of bacteria and pH levels in the vagina, leading to infections.
4. Dry Yourself Thoroughly
- After cleaning: Always dry the genital area thoroughly after washing. Moisture can encourage the growth of bacteria, leading to infections like yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis.
5. Wear Breathable Clothing
- Cotton underwear: Cotton underwear is breathable and reduces moisture, preventing irritation or the growth of bacteria. Avoid tight-fitting synthetic materials that can trap moisture.
- Avoid wearing the same pad/tampon for too long: If you are unable to change your pad or tampon, consider using a menstrual cup or period panties as alternatives for longer wear.
6. Proper Disposal of Sanitary Products
- Dispose of sanitary items hygienically: Always dispose of used pads, tampons, and menstrual cups properly. Wrap them securely before discarding them in a waste bin. Never flush sanitary products down the toilet, as this can cause blockages and environmental harm.
7. Stay Hydrated and Maintain Good Nutrition
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to help your body cope with the hormonal fluctuations during menstruation.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet can help maintain your menstrual health and ease symptoms such as cramps, bloating, and mood swings. Include fiber, iron, and vitamins to support your body during menstruation.
8. Be Aware of Abnormal Symptoms
- Pain: Mild menstrual cramps are normal, but severe pain may signal underlying issues, such as endometriosis or fibroids. Don’t ignore significant discomfort.
- Excessive bleeding: If you experience heavy bleeding (soaking through a pad or tampon every 1–2 hours), it’s important to consult a healthcare provider as it may indicate a medical condition.
- Odor or unusual discharge: A foul odor or abnormal discharge during menstruation may indicate an infection, and you should seek medical advice if it persists.
9. Practice Safe Sex During Menstruation
- Protection during menstruation: While it’s safe to have sex during menstruation, use protection (such as condoms) to prevent the transmission of infections, especially if you or your partner have a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
10. Track Your Menstrual Cycle
- Know your cycle: Tracking your menstrual cycle can help you understand what’s normal for your body. It can also help in identifying any irregularities or issues, such as missed periods or unusual bleeding patterns, which may require medical attention.
11. Consult a Doctor Regularly
- Regular check-ups: Regular gynecological check-ups can help detect and prevent any underlying issues related to menstrual health, like fibroids, hormonal imbalances, or infections.
By following these hygiene practices, you can ensure that your menstrual health remains optimal. Paying attention to hygiene, being aware of your body’s signals, and using the right products are essential steps to avoiding discomfort and potential health issues.